In the fast-paced environment of a packaging production hall, efficiency and reliability are paramount.
Two successful methods used to improve productivity are:
- Measuring Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), and
- Implementing Total Productive Maintenance (TPM).
While measuring OEE lets you see the scoreboard, to make significant changes, you need to get in the game.
This is where TPM and astute technology selection are crucial.
Advanced packaging automation machines, coupled with software solutions that can integrate existing and new machinery, can substantially improve a packaging production line.
Understanding OEE
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a crucial metric that evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of a manufacturing process.
It is calculated by multiplying the availability, performance, and quality rates.
Essentially, OEE provides insights into how well a production line is functioning compared to its full potential.
- Availability: This component measures the actual production time versus the planned production time, accounting for any downtime.
- Performance: This assesses whether the equipment is running at its maximum speed.
- Quality: This considers the proportion of good products produced versus the total products produced.
By focusing on OEE, manufacturers can identify and address the root causes of inefficiencies, thus enhancing productivity.
The Role of TPM
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a holistic approach to maintenance that aims to achieve perfect production with no breakdowns, slowdowns, or defects.
It involves all employees, from operators to managers, in maintaining and improving equipment.
Key Pillars of TPM:
- Autonomous Maintenance: Operators are trained to perform routine maintenance tasks, which helps detect potential issues early.
- Planned Maintenance: Scheduled maintenance activities are planned based on historical data and machine condition.
- Quality Maintenance: Focuses on maintaining equipment to ensure it consistently produces high-quality products.
- Focused Improvement: Small groups work on targeted improvements to enhance specific aspects of the production process.
- Training and Education: Continuous training ensures that all employees are equipped with the skills needed to maintain and improve equipment.
Integrating OEE and TPM into packaging production lines can lead to significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and product quality.
A Case Study
A leading beverage manufacturer faced challenges with their packaging line, including frequent downtime, inconsistent production speed, and quality control issues.
The company's goal was to enhance overall productivity, reduce waste, and maintain high product quality.
To this end, it sought Foodmach's expertise to revamp its production processes.
Assessment and Diagnostic Phase:
Foodmach's team conducted a comprehensive assessment of the manufacturer's packaging line.
This included:
- Detailed Analysis: Analysing the current state of machinery and identifying key bottlenecks.
- OEE Evaluation: Calculating OEE to measure the effectiveness of existing equipment. The initial OEE score was 65%, a good score but indicating significant room for improvement.
- TPM Readiness: Evaluating the manufacturer's readiness for implementing TPM practices.
Implementation Phase:
- Customised Automation Solutions:
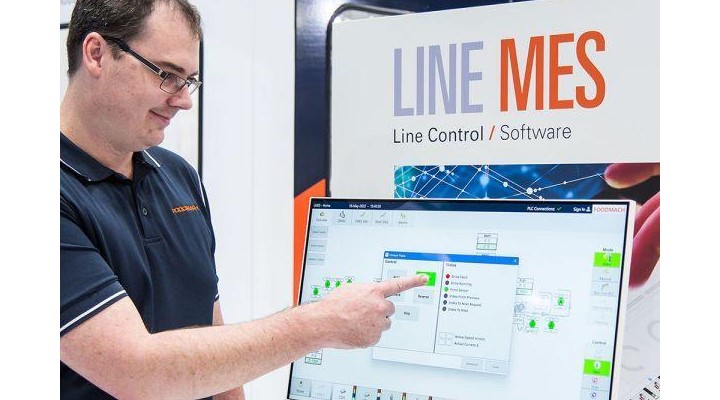
- Integration of Advanced Control Systems: Foodmach installed software systems to control the line and monitor real-time OEE metrics. This allowed for immediate identification and rectification of performance issues.
- Equipment Upgrades: Some of the existing machinery was upgraded with more reliable and efficient machines, increasing capacity and reducing the likelihood of breakdowns.
- TPM Practices:
- Autonomous Maintenance Training: Operators were trained to perform basic maintenance tasks and identify early signs of equipment wear and tear. This empowered them to take ownership of their machines, leading to quicker issue resolution.
- Scheduled Maintenance: A planned maintenance schedule was developed based on the equipment's historical performance data. This proactive approach minimised unexpected downtimes.
- Quality Maintenance Programs: Continuous monitoring and adjustments ensured that the equipment consistently produced high-quality products, reducing defects and rework.
- Performance Monitoring and Continuous Improvement:
- Real-Time Data Analysis: The control systems provided live data on performance, allowing the team to make informed decisions quickly.
- Focused Improvement Teams: Small teams were formed to address specific areas of improvement, such as reducing changeover times and optimising equipment settings.
Results Achieved:
- Increased Availability:
- Reduced Downtime: Downtime was reduced by 20% due to the combination of autonomous and planned maintenance practices. The new control systems helped in quickly diagnosing and fixing issues, minimising production stoppages.
- Enhanced Performance:
- Improved Production Speed: By optimising equipment settings, reducing micro-stops and improving conveyor controls, the production rate increased by 10%. This improvement was crucial in meeting higher production targets without compromising quality.
- Improved Quality:
- Reduced Defects: Quality maintenance programs significantly reduced product defects. The manufacturer saw a 10% decrease in rework rates, which translated into cost savings and better resource utilisation.
- Overall OEE Improvement:
- OEE Score: The cumulative effect of these improvements was reflected in the OEE score, which rose from 65% to 80%. This marked a substantial leap in the production line's efficiency and effectiveness.
- Cost Savings and ROI:
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: The shift from reactive to proactive maintenance reduced maintenance costs by 15%. The initial investment in upgrading equipment and training staff showed a high return on investment within the first year.
- Employee Empowerment and Engagement:
- Increased Engagement: Operators and maintenance staff felt more engaged and empowered due to their active involvement in maintenance and improvement processes. This led to higher job satisfaction and lower turnover rates.
Conclusion
Overall Equipment Effectiveness and Total Productive Maintenance are powerful methodologies that can transform packaging production lines.
By leveraging advanced automation, real-time data monitoring, comprehensive training programs, and informed selection of packaging machinery, companies like Foodmach enable manufacturers to achieve significant improvements in productivity, quality, and cost-efficiency.
This holistic approach not only addresses immediate issues but also sets the foundation for sustained operational excellence, ensuring that production lines are running at peak efficiency and ready to meet the demands of a competitive market.